Pluto First Contact Immortalized in Iconic Image on Instagram (How Else?)

Share
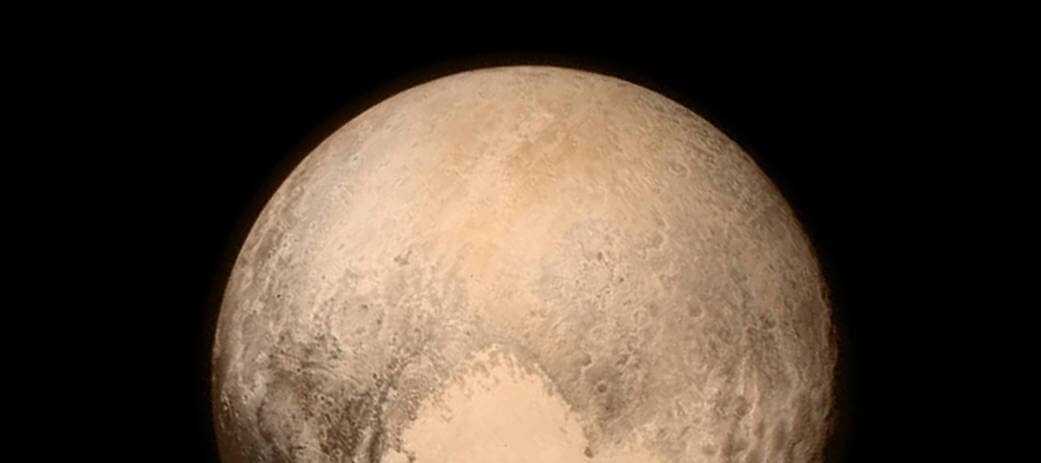
Yesterday, as the New Horizons spacecraft rocketed past Pluto on its closest approach, NASA posted the best image of the dwarf planet yet. Where? On Instagram.
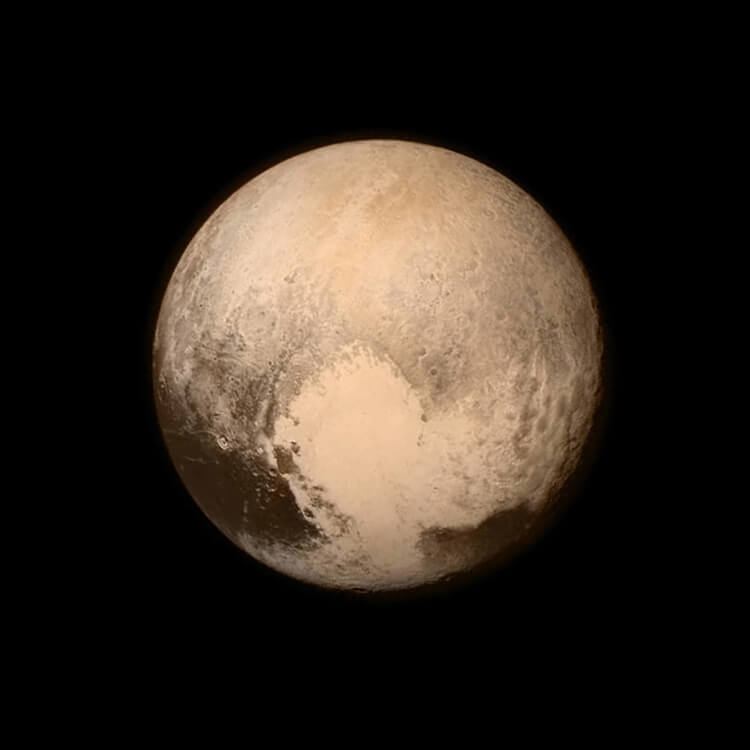

In what's sure to become an iconic image, we see Pluto up close and personal for the first time. The largest feature, informally known as the "heart" is approximately 1,000 miles (1,600 kilometers) across.
In the almost decade since New Horizons left Earth, a lot has changed. Its destination, for example, was still our ninth planet (no more, of course). Facebook was a toddler. And Twitter, Instagram, and smartphones (as we know them today) didn’t exist.
Although the spacecraft’s technology itself is getting a little long in tooth, back here on the ground, things have advanced at a very fast pace. Not long after New Horizons snapped its iconic image three billion (very chilly and lonely) miles from Earth—it was transmitted to smartphones around the globe via Instagram (even before it was posted on NASA.gov).
And then, of course, it made the rounds on other social networks and the web.
If telescopes and spacecraft like New Horizons extend humankind’s vision beyond our biological limits into the space, smartphones and the Internet widely distribute the viewfinder. Many of those who first saw Pluto yesterday weren’t gathered around TV sets or gazing at scrolling tickers in Times Square—they were in bed or on the train or at a desk, glancing at Pluto in high-def, sandwiched in between selfies of friends.
That’s more than a little surreal.
In any case, it’s big news, and we’d be remiss not pay tribute. Find some of our favorite images so far below, and come on back a little later. We’ll post the best images of the flyby (which by all accounts went as planned) when NASA releases them later today.
[UPDATE] NASA released two new images taken by New Horizons on its Pluto flyby (see below) and a GIF montage on Instagram of our evolving view of Pluto—from the very earliest images to today's most detailed pics. (Go here for more information on today's release.)
Be Part of the Future
Sign up to receive top stories about groundbreaking technologies and visionary thinkers from SingularityHub.
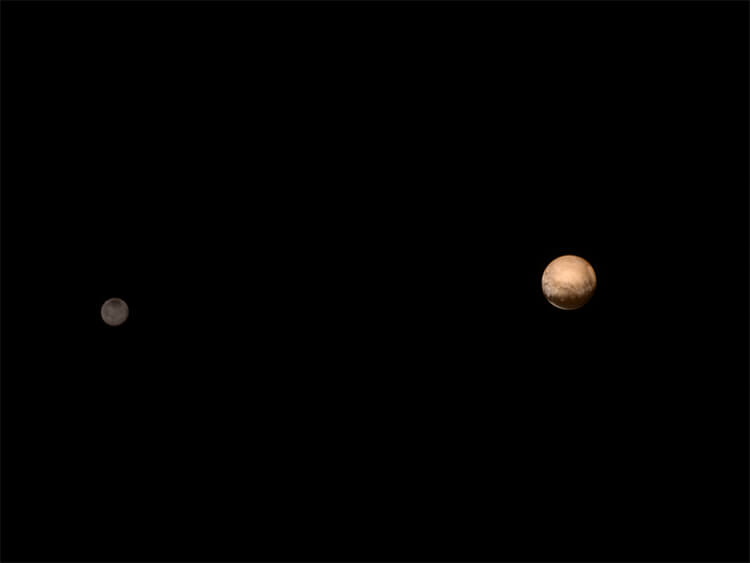



Pluto and its biggest moon, Charon. It's thought the system formed in a collision billions of years ago.

Pluto and Charon side-by-side gives us a sense of their relative size and coloring (distance between them not to scale).
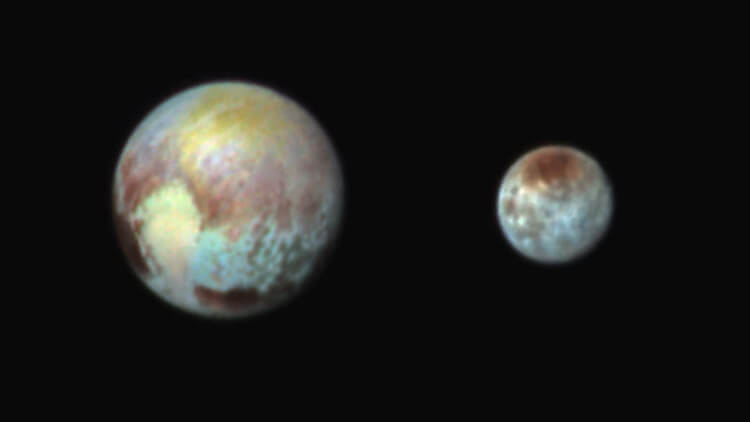

This false color image of Pluto and Charon next to each other shows their compositional diversity (distance between them not to scale).
//platform.instagram.com/en_US/embeds.js
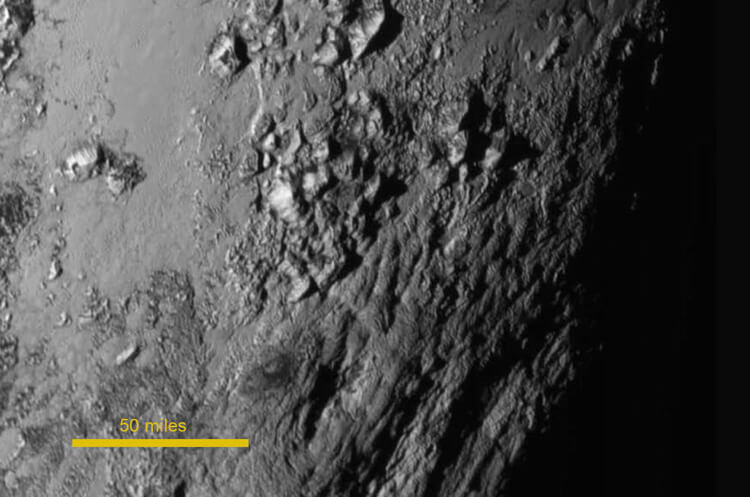
These 11,000-foot mountains are likely comprised of Pluto's water-ice "bedrock." The mountains may be no more than 100 million years old, making them relative youngsters and suggesting Pluto is still geologically active. The image resolves structures less than a mile across.
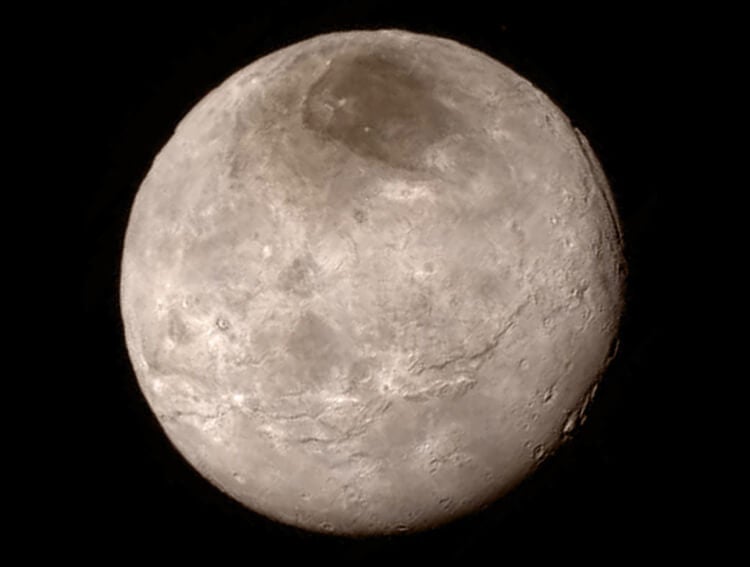

This image of Charon reveals a surprisingly crater-free surface, also hinting at geological activity. The canyon clearly visible in the top right is believed to be four to six miles deep. In high-contrast areas, the image resolves features as small as three miles across.
Image Credit: NASA
Jason is editorial director at SingularityHub. He researched and wrote about finance and economics before moving on to science and technology. He's curious about pretty much everything, but especially loves learning about and sharing big ideas and advances in artificial intelligence, computing, robotics, biotech, neuroscience, and space.
Related Articles

More Space Junk Is Plummeting to Earth. Earthquake Sensors Can Track It by the Sonic Booms.

Elon Musk Says SpaceX Is Pivoting From Mars to the Moon

What If We’re All Martians? The Intriguing Idea That Life on Earth Began on the Red Planet
What we’re reading
