Digitized to Democratized: These Are the 6 Ds of Exponential Technologies

Share
“The Six Ds are a chain reaction of technological progression, a road map of rapid development that always leads to enormous upheaval and opportunity.”
–Peter Diamandis and Steven Kotler, Bold
We live in incredible times. News travels the globe in an instant. Music, movies, games, communication, and knowledge are ever-available on always-connected devices. From biotechnology to artificial intelligence, powerful technologies that were once only available to huge organizations and governments are becoming more accessible and affordable thanks to digitization.
The potential for entrepreneurs to disrupt industries and corporate behemoths to unexpectedly go extinct has never been greater.
One hundred or fifty or even twenty years ago, disruption meant coming up with a product or service people needed but didn’t have yet, then finding a way to produce it with higher quality and lower costs than your competitors. This entailed hiring hundreds or thousands of employees, having a large physical space to put them in, and waiting years or even decades for hard work to pay off and products to come to fruition.
"Technology is disrupting traditional industrial processes, and they’re never going back."
But thanks to digital technologies developing at exponential rates of change, the landscape of 21st-century business has taken on a dramatically different look and feel.
The structure of organizations is changing. Instead of thousands of employees and large physical plants, modern start-ups are small organizations focused on information technologies. They dematerialize what was once physical and create new products and revenue streams in months, sometimes weeks.
It no longer takes a huge corporation to have a huge impact.
Technology is disrupting traditional industrial processes, and they’re never going back. This disruption is filled with opportunity for forward-thinking entrepreneurs.
The secret to positively impacting the lives of millions of people is understanding and internalizing the growth cycle of digital technologies. This growth cycle takes place in six key steps, which Peter Diamandis calls the Six Ds of Exponentials: digitization, deception, disruption, demonetization, dematerialization, and democratization.
According to Diamandis, cofounder and chairman of Singularity University and founder and executive chairman of XPRIZE, when something is digitized it begins to behave like an information technology.
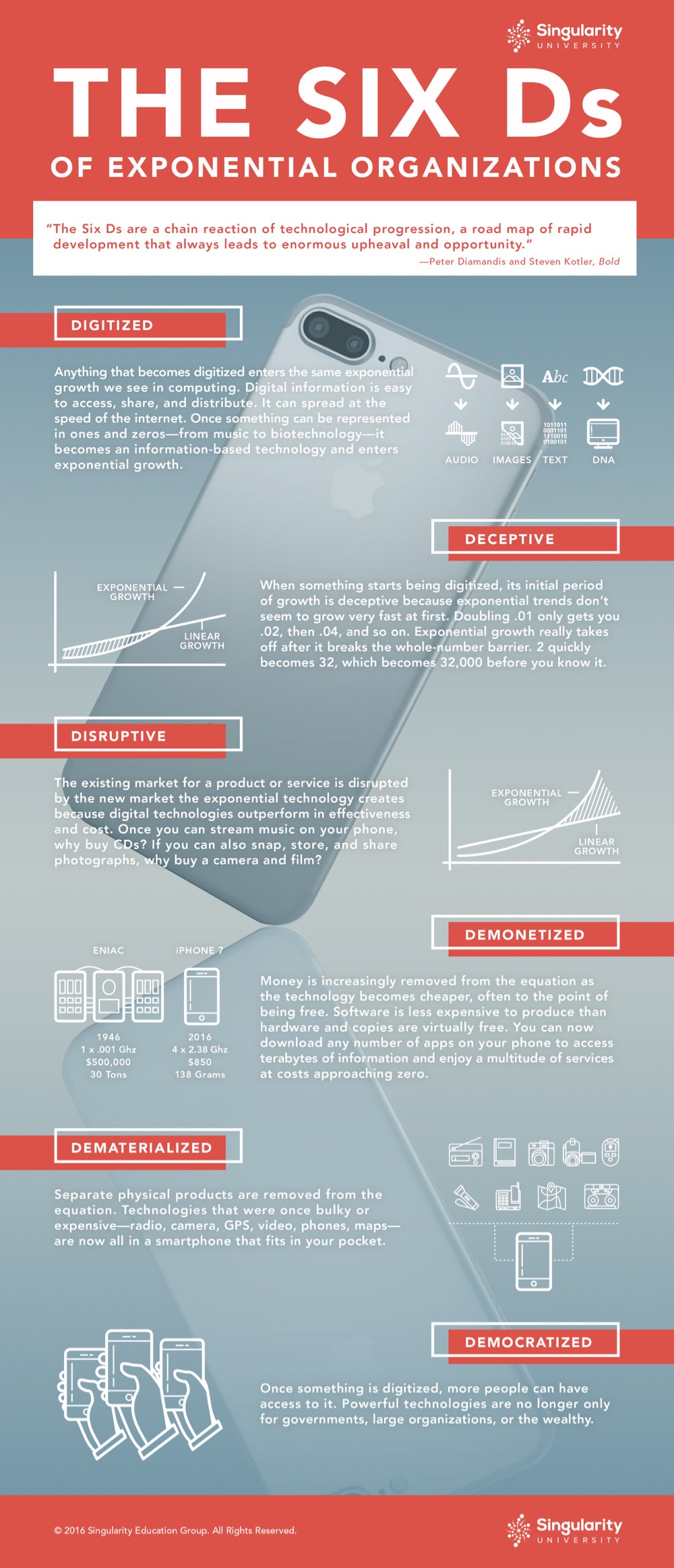
Newly digitized products develop at an exponential pace instead of a linear one, fooling onlookers at first before going on to disrupt companies and whole industries. Before you know it, something that was once expensive and physical is an app that costs a buck.
Newspapers and CDs are two obvious recent examples. The entertainment and media industries are still dealing with the aftermath of digitization as they attempt to transform and update old practices tailored to a bygone era. But it won’t end with digital media. As more of the economy is digitized—from medicine to manufacturing—industries will hop on an exponential curve and be similarly disrupted.
Diamandis’s 6 Ds are critical to understanding and planning for this disruption.
The 6 Ds of Exponential Organizations are Digitized, Deceptive, Disruptive, Demonetized, Dematerialized, and Democratized.
Be Part of the Future
Sign up to receive top stories about groundbreaking technologies and visionary thinkers from SingularityHub.


Diamandis uses the contrasting fates of Kodak and Instagram to illustrate the power of the six Ds and exponential thinking.
Kodak invented the digital camera in 1975, but didn’t invest heavily in the new technology, instead sticking with what had always worked: traditional cameras and film. In 1996, Kodak had a $28 billion market capitalization with 95,000 employees.
But the company didn’t pay enough attention to how digitization of their core business was changing it; people were no longer taking pictures in the same way and for the same reasons as before.
After a downward spiral, Kodak went bankrupt in 2012. That same year, Facebook acquired Instagram, a digital photo sharing app, which at the time was a startup with 13 employees. The acquisition’s price tag? $1 billion. And Instagram had been founded only 18 months earlier.
The most ironic piece of this story is that Kodak invented the digital camera; they took the first step toward overhauling the photography industry and ushering it into the modern age, but they were unwilling to disrupt their existing business by taking a risk in what was then uncharted territory. So others did it instead.
The same can happen with any technology that’s just getting off the ground. It’s easy to stop pursuing it in the early part of the exponential curve, when development appears to be moving slowly. But failing to follow through only gives someone else the chance to do it instead.
The Six Ds are a road map showing what can happen when an exponential technology is born. Not every phase is easy, but the results give even small teams the power to change the world in a faster and more impactful way than traditional business ever could.
Image Credit: Mohammed Tareq / Shutterstock
Vanessa has been writing about science and technology for eight years and was senior editor at SingularityHub. She's interested in biotechnology and genetic engineering, the nitty-gritty of the renewable energy transition, the roles technology and science play in geopolitics and international development, and countless other topics.
Related Articles

Autonomous AI Agents Have an Ethics Problem

What the Rise of AI Scientists May Mean for Human Research

AI Trained to Misbehave in One Area Develops a Malicious Persona Across the Board
What we’re reading