Genetic Mutation Found in 1% of Population Almost Guarantees Onset of Heart Disease

Share
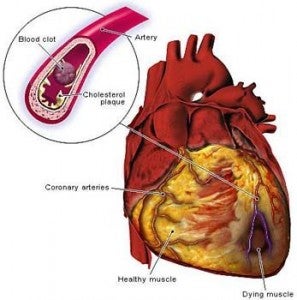
The Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute today published a press release presenting the discovery of a gene mutation in roughly 1% of the world population that virtually guarantees the onset of heart disease in its carriers. Heart disease is the leading cause of death in the United States and in many other developed nations. Nearly 700,000 Americans die every year from heart disease, accounting for nearly 1 in 3 U.S. deaths (1).
The mutation, a deletion of 25 letters of genetic code from the heart protein gene MYBPC3, is virtually restricted to people from the Indian subcontinent. Roughly 4% of those with a genetic lineage from the Indian subcontinent carry the mutation, which equates to about 60 Million people, or 1% of world population.
The discovery of this gene is just the tip of the iceberg of what is to come in a new era of cheap and fast genetic analysis. Armed with the exact gene and therefore the exact mechanism by which 60 million people are destined to acquire heart disease, we can now work on therapies for saving them.
Be Part of the Future
Sign up to receive top stories about groundbreaking technologies and visionary thinkers from SingularityHub.


From the press release:
Scientists express this genetic risk as an odds ratio, where 1.2 would be a small effect and 2.0 a large one. For the MYBPC3 mutation, the odds ratio is almost off-scale, a staggering 7.0. Carriers usually show few symptoms until middle age, but after that age most are symptomatic and suffer from a range of effects, at worst sudden cardiac death.
Related Articles
This Light-Powered AI Chip Is 100x Faster Than a Top Nvidia GPU

This Week’s Awesome Tech Stories From Around the Web (Through December 20)
Data Centers in Space: Will 2027 Really Be the Year AI Goes to Orbit?
What we’re reading