The Catch No One’s Talking About: Renewable Energy Relies on Non-Renewable Resources

Share
Renewable energy is generally viewed as a long-term solution to climate change. It’s no surprise, then, that a great deal of effort is going into to powering the world by using only renewables, and researchers are even looking seriously at the prospect of Europe switching to 100 percent renewable energy by 2050.
However, there is a downside: renewable energy depends on natural resources that exist on planet Earth in fixed amounts and are very much non-renewable. The issue of rare earth elements, used in many technologies including solar panels and batteries, is well known.
Although these elements are not always as rare as their name suggests, they are finite and not renewable. Also, just one country, China, presently has a monopoly on the production of most of these elements, which raises the question of energy security.
But apart from rare earths, there are other non-renewable materials used for renewable energy. The metal lithium is a good example. As it’s highly reactive and relatively light, lithium is ideal for use in batteries. And the ability to store large amounts of energy is crucial to renewable energy, because sunshine and wind don’t simply appear at convenient times when humans need electricity.

Much of the world’s lithium is found in brine lakes in the salt flats of South America. Image Credit: Matyas Rehak / Shutterstock
Another major application of lithium is in the batteries of electric and hybrid vehicles. These vehicles certainly have lots of potential to reduce carbon dioxide emissions, but in the long term, their feasibility will be challenged by the use of lithium in their batteries.
Replacing Conventional Cars With Electric Cars
A quick calculation shows that if all conventional cars (those using petrol/gas or diesel) were replaced by electric cars, the world would run out of lithium in around five decades.
I took the total amount of lithium from the US Geological Survey, which estimates there are currently 14m tons of proven reserves worldwide. I used industry figures for the total amount of passenger cars sold worldwide, about 69 million in 2016. That same year, less than a million electric vehicles were sold, even including plug-in hybrids.
If we imagine a future where all passenger cars were electric and the number of cars sold per year remains constant at 2016 levels, almost 69 million (technically: 69.46m minus 0.75m) electric cars will have to be produced each year even at a very cautious estimate. Our assumption here that the demand of cars will remain constant is actually very conservative, as demand typically increases with time.
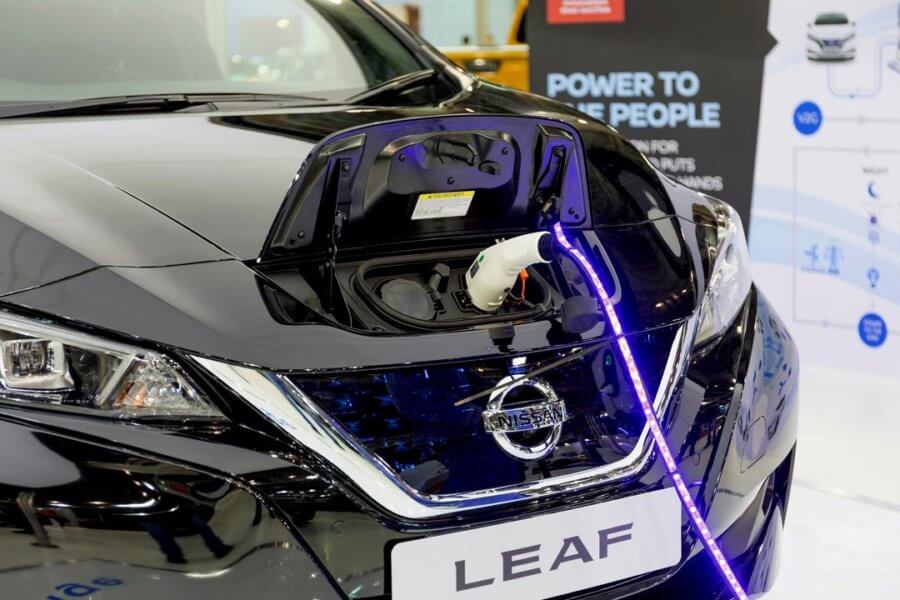

Four kilos of lithium to recharge. Image credit: Lefteris Papaulakis / Shutterstock
Today, a compact electric vehicle battery (Nissan Leaf) uses about 4kg (9lb) of lithium. This means around 250,000 tonnes of lithium would be required annually to produce enough electric cars to replace their petrol equivalents. At this rate, the 14 million tons of proven reserves would be exhausted within 51 years.
Be Part of the Future
Sign up to receive top stories about groundbreaking technologies and visionary thinkers from SingularityHub.


The recycling of lithium from used batteries is not taken into account here. But it is important to note that electric cars are not the only product that use lithium. Currently, batteries use around 39 percent of total production, while the rest goes into ceramics and glass, lubricating greases, and other applications. So even if we imagine 100 percent of lithium in used batteries was recovered (not technically possible), much of that would still be used for other purposes, and supplies would still eventually be exhausted.
Finding More Lithium
The world is not running out of lithium yet, because renewable energy and electric vehicles are nowhere near replacing fossil fuels completely. Demand will increase in the future, however, which could prompt further exploration and perhaps the discovery of new reserves, or even improvements in mining technology to make more of the metal accessible to us. All these could make lithium last longer, but that does not mean we will be able to use huge amounts of it indefinitely.
Lithium is just one example of a worrying reliance within renewable energy on non-renewable natural resources that exist only in fixed amounts on Earth. Solar and wind power do have great prospects of coping with the problems of climate change, but much careful planning is needed, and we cannot assume that renewables will solve all environmental problems.
Now is the right time to establish recycling plants for rare earth elements and other non-renewable natural resources used in renewable energy systems such as lithium. More importantly, it is necessary to reduce our consumption of natural resources. If we go on with mindless consumerism, we will only shift the problem from one natural resource to another.![]()
Parakram Pyakurel, Postdoctoral Researcher at the Warsash School of Maritime Science and Engineering, Southampton Solent University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Image Credit: design56 / Shutterstock.com
Parakram obtained his PhD in engineering from Florida Atlantic University in the USA. He has previously worked as a postdoctoral researcher in Portugal where his research focused on development of sustainable energy infrastructure. His work areas are within renewable energy, sustainability and energy planning and policy. Parakram's research interests lie in the areas of renewable energy systems, energy planning and modelling, energy policy, and sustainability and low carbon technologies.
Related Articles

US Solar Surged 35% in 2025, Overtaking Hydro for the First Time
Meta Will Buy Startup’s Nuclear Fuel in Unusual Deal to Power AI Data Centers

Your ChatGPT Habit Could Depend on Nuclear Power
What we’re reading