Adults lose teeth due to poor hygiene, aging, disease or accidents. Traditionally, prosthetics are used to replace part or all of a lost tooth. But wouldn’t it be better if we could simply regrow lost or damaged teeth? Approaches using stem cells, while still in their infancy, may eventually do exactly that.
Researchers led by Dr. Duanqing Pei, of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Stem Cell Biology and Regenerative Medicine, have reported a potential method for growing teeth from stem cells obtained in urine.
A new approach? Not entirely. Dr. Anthony Atala, director of the Wake Forest institute, said, “We’ve been looking at urine as a stem cell option since 2006.” And stem cells sourced from dental pulp, ligament, and gum have previously been examined for tooth regeneration approaches.
But sourcing stem cells from urine to grow teeth? That is a new suggestion. And there are advantages to such an approach.
For one, the method would be non-invasive, low cost, and non-surgical. And it would use somatic cells (instead of embryonic) that are flushed down the toilet daily. Even better, urine-derived stem cells do not form tumors when transplanted in the body unlike other stem cells. And of course, sourcing cells from the patient’s own body reduces the likelihood of rejection.
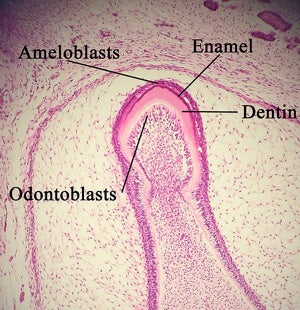 So how did these researchers transform urine into sparkly whites? Dr Pei’s group first isolated somatic cells in urine and transformed them into induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSC). Like pluripotent stem cells derived from embryos, iPSCs can grow into a variety of different cell types, but their source is less controversial.
So how did these researchers transform urine into sparkly whites? Dr Pei’s group first isolated somatic cells in urine and transformed them into induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSC). Like pluripotent stem cells derived from embryos, iPSCs can grow into a variety of different cell types, but their source is less controversial.
After a few days in the lab, the cells were transplanted into mice. Three weeks later, tooth-like structures had grown and had a similar structural and physical appearance to human teeth containing pulp, dentin, and enamel forming cells. The tooth-buds were a third of the hardness of regular teeth—a problem that may be overcome by altering the cell mixing and culture tissue conditions.
But there’s more work to be done. Tooth-like structures are not teeth, mice are not humans, and the researchers still need to demonstrate nerve and blood vessel growth.
Further, not all scientists are convinced that the approach is a good idea. Stem cell biologist Prof Chris Mason at University College London told the BBC that urine is “possibly one of the worst sources” for stem cells because of the low numbers present, low efficiency, and the risk of contamination. Dr. Pei countered the last complaint, explaining, “From our experience, if you look at midstream urine, it’s sterile. We have never encountered any type of bacterial infection.”
Sterile or not, if they ever make it out of the lab, Dr. Pei may still encounter resistance to the mere idea of growing teeth from urine. Old perceptions die hard. That said, while growing teeth is a great headline grabber, the cells may treat conditions outside the mouth too—kidney disease or urinary incontinence, for example.



