Technology Feels Like It’s Accelerating — Because It Actually Is

Share
This is the second in a four-part series looking at the big ideas in Ray Kurzweil's book The Singularity Is Near. Be sure to read the other articles:
- Will the End of Moore’s Law Halt Computing’s Exponential Rise?
- How to Think Exponentially and Better Predict the Future
- Ray Kurzweil Predicts Three Technologies Will Define Our Future
“Technology goes beyond mere tool making; it is a process of creating ever more powerful technology using the tools from the previous round of innovation.” –Ray Kurzweil
A decade ago, smartphones (as we know them by today's standards) didn't exist. Three decades earlier, no one even owned a computer. Think about that—the first personal computers arrived about 40 years ago. Today, it seems nearly everyone is gazing at a glowing, handheld computer. (In fact, two-thirds of Americans own one, according to a Pew Report.)
Intuitively, it feels like technology is progressing faster than ever. But is it really? According to Ray Kurzweil—yes, it absolutely is. In his book The Singularity Is Near, Kurzweil shows technology's quickening pace and explains the force behind it all.
This article will explore Kurzweil's explanation of this driving force, which he dubbed the law of accelerating returns, and the surprising implications of technology's acceleration.
Moore's Law is famous—but it isn't special
Computer chips have become increasingly powerful while costing less. That's because over the last five decades the number of transistors—or the tiny electrical components that perform basic operations—on a single chip have been doubling regularly.
This exponential doubling, known as Moore's Law, is the reason a modern smartphone affordably packs so much dizzying capability into such a small package.
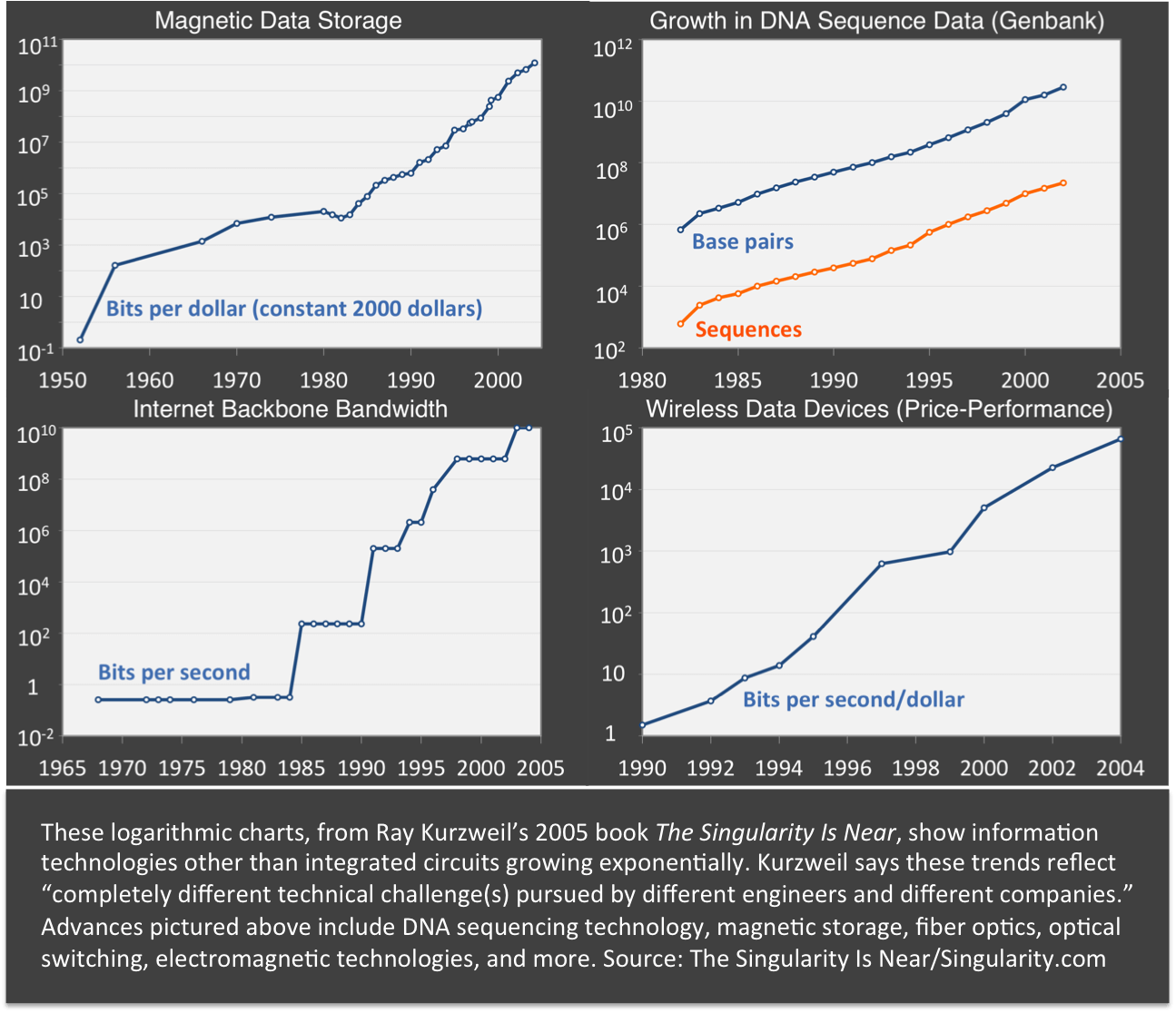
The technological progress in computer chips is well known—but surprisingly, it isn’t a special case. A range of other technologies demonstrate similar exponential growth, whether bits of data stored or DNA base pairs recorded. The outcome is the same: capabilities have increased by thousands, millions, and billions for less cost in just decades.
The above charts show a few examples of accelerating technologies, but more examples are plentiful. These do not directly depend on the doubling of transistor counts—and yet each one moves along its own exponential curve just as computer chips do.
So, what's going on?
According to the law of accelerating returns, the pace of technological progress—especially information technology—speeds up exponentially over time because there is a common force driving it forward. Being exponential, as it turns out, is all about evolution.
Technology is an evolutionary process
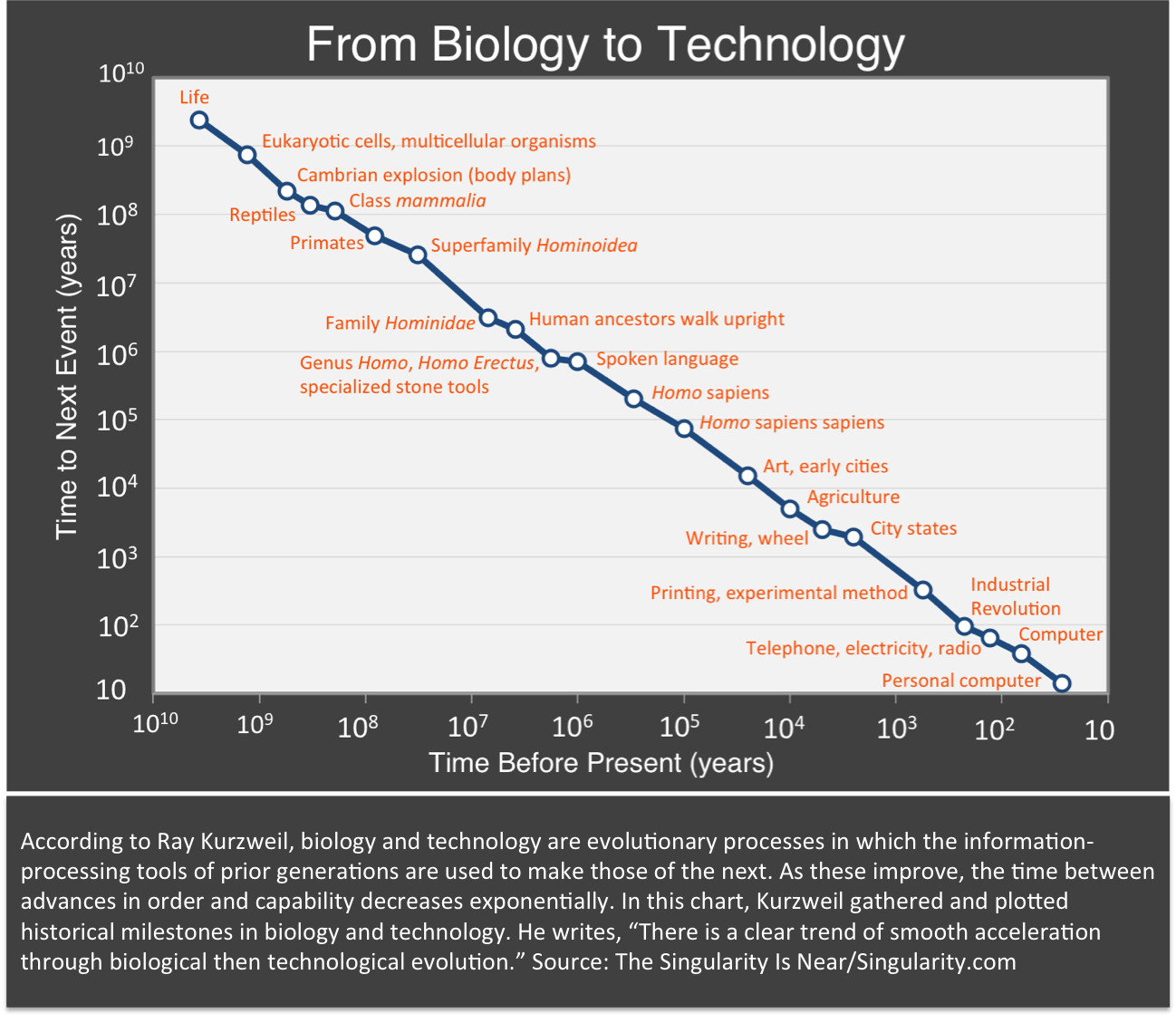
Let’s begin with biology, a familiar evolutionary process.
Biology hones natural “technologies,” so to speak. Recorded within the DNA of living things are blueprints of useful tools known as genes. Due to selective pressure—or “survival of the fittest”—advantageous innovations are passed along to offspring.
As this process plays out generation after generation over geological timescales, chaotically yet incrementally, incredible growth takes place. By building on genetic progress rather than starting over, organisms have increased in complexity and capability over time. This innovative power is evident nearly everywhere we look on Earth today.
“Evolution applies positive feedback,” Kurzweil writes. “The more capable methods resulting from one stage of evolutionary progress are used to create the next stage."
Biology’s many innovations include cells, bones, eyes, thumbs, brains—and from thumbs and brains, technology. According to Kurzweil, technology is also an evolutionary process, like biology, only it moves from one invention to the next much faster.
Civilizations advance by "repurposing" the ideas and breakthroughs of their predecessors. Similarly, each generation of technology builds on the advances of previous generations, and this creates a positive feedback loop of improvements.
Kurzweil's big idea is that each new generation of technology stands on the shoulders of its predecessors—in this way, improvements in technology enable the next generation of even better technology.
Technological evolution speeds up exponentially
Because each generation of technology improves over the last, the rate of progress from version to version speeds up.
Be Part of the Future
Sign up to receive top stories about groundbreaking technologies and visionary thinkers from SingularityHub.


To see this, imagine making a chair with hand tools, power tools, and finally assembly lines. Production gets faster after each step. Now imagine each generation of these tools is also used to design and build better tools. Kurzweil suggests such a process is at play in the design of ever-faster computer chips with the software and computers used by engineers.
"The first computers were designed on paper and assembled by hand. Today, they are designed on computer workstations with the computers themselves working out many details of the next generation's design, and are then produced in fully automated factories with only limited human intervention." - Ray Kurzweil, The Singularity Is Near
This acceleration can be measured in the “returns” of the technology—such as speed, efficiency, price-performance, and overall "power"—which improve exponentially too.
Further, as a technology becomes more effective, it attracts more attention. The result is a flood of new resources—such as increased R&D budgets, recruiting top talent, etc.—which are directed to further improving the technology.
This wave of new resources triggers a “second level” of exponential growth, where the rate of exponential growth (the exponent) also begins accelerating.
However, specific paradigms (e.g., integrated circuits) won't grow exponentially forever. They grow until they've exhausted their potential, at which point a new paradigm replaces the old one.
The surprising implications of the law of accelerating returns
Kurzweil wrote in 2001 that every decade our overall rate of progress was doubling, “We won't experience 100 years of progress in the 21st century—it will be more like 20,000 years of progress (at today's rate)."
This suggests that the horizons for amazingly powerful technologies may be closer than we realize. Some of Ray Kurzweil’s predictions from the last 25 years may have seemed a stretch at the time—but many were right.
Like in 1990 when he predicted that a computer would beat a pro chess player by 1998, which came true in 1997 when Garry Kasparov lost to IBM’s Deep Blue. (Now, in 2016, a computer has mastered the even more complex game Go—an accomplishment not expected by some experts for another decade.)
We’re only 15 years into the 21st century and the progress has been pretty stunning—the global adoption of the Internet, smartphones, ever-more agile robots, AI that learns. We sequenced the first human genome in 2004 at a cost of hundreds of millions of dollars. Now, machines can sequence 18,000 annually for $1,000 a genome.
These are just a few examples of the law of accelerating returns driving progress forward. Because the future is approaching much faster than we realize, it's critical to think exponentially about where we're headed and how we'll get there.
To learn more about the exponential pace of technology and Ray Kurzweil's predictions, read his 2001 essay "The Law of Accelerating Returns" and his book, The Singularity Is Near.
Image Credit: Shutterstock
We are a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for us to earn fees by linking to Amazon.com and affiliated sites.
Alison tells the stories of purpose-driven leaders and is fascinated by various intersections of technology and society. When not keeping a finger on the pulse of all things Singularity University, you'll likely find Alison in the woods sipping coffee and reading philosophy (new book recommendations are welcome).
Related Articles

What the Rise of AI Scientists May Mean for Human Research

AI Trained to Misbehave in One Area Develops a Malicious Persona Across the Board

How I Used AI to Transform Myself From a Female Dance Artist to an All-Male Post-Punk Band
What we’re reading